NDT (UT) Theory and Demonstration

Language
English
5 Views
Share
Coming in March, 2025
-
-
This course format is where trainer will explain you the subject via online live session. Date and time are not decided yet but it will be planned within next 2 weeks after you enroll & pay for this course. Get in touch with our team if any clarification is required.
₹ 499
online

₹ 499
Why do you enroll
Key topics covered
Course details
Course tags
Why do you enroll
Mastering Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) techniques, specifically Ultrasonic Testing (UT), can advance your career in quality control, inspection, and testing, leading to roles like NDT Technician, Quality Inspector, or Testing Engineer, with median salaries ranging from $60,000 to over $100,000. You'll gain expertise to detect internal defects and measure material thickness, ensuring product integrity and reliability in industries like aerospace, energy, and manufacturing, where safety and precision are critical. This certification will also enable you to work on complex components, such as pipelines and pressure vessels, making you a highly sought-after professional.
Show more
Key topics covered
Introduction to NDT and Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Overview of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) and its role in quality control and material inspection
Basic principles of Ultrasonic Testing (UT) and its advantages over other NDT methods
Common applications of UT in industries such as aerospace, manufacturing, oil & gas, and construction
Fundamentals of Ultrasonics
Principles of sound waves and how they propagate through different materials
Key concepts: frequency, wavelength, velocity, and attenuation
Types of ultrasonic waves: Longitudinal waves, shear waves, and surface waves
Ultrasonic Testing Equipment and Transducers
Overview of UT equipment: Ultrasonic flaw detectors, transducers, and probes
Types of transducers: Contact, angle, and immersion probes
Selection of transducer frequency based on material thickness, type, and defect characteristics
Calibration and setup of ultrasonic equipment
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation and Interaction with Materials
How ultrasonic waves travel through different materials (metals, composites, etc.)
Reflection, refraction, and scattering of ultrasonic waves at material boundaries
Effect of material properties (e.g., grain structure, density, temperature) on wave propagation
Techniques for Defect Detection
How UT detects discontinuities such as cracks, porosity, inclusions, and laminations
Types of UT inspection techniques:
Pulse-echo method (for thickness measurement and flaw detection)
Through-transmission method (for bond integrity and large component inspections)
Time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) and phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT)
Understanding how defects affect wave propagation and result in reflections or scattering
Inspection Procedures and Settings
Step-by-step process for performing an ultrasonic inspection
Surface preparation and coupling techniques for optimal signal transmission
Common UT scanning methods: Straight beam, angle beam, and spiral scanning
Use of calibration blocks and reference standards to ensure accuracy
Interpreting Ultrasonic Signals
Understanding the signals on the UT display: amplitude, time, and signal shape
Identifying defect types and characteristics from signal responses
Interpreting signal changes and differentiating between real defects and benign material features
Use of A-scan, B-scan, and C-scan displays for different types of analysis
Safety Considerations in UT
Safe handling of ultrasonic equipment, including high-voltage and high-frequency aspects
Radiation safety and precautions, particularly with certain transducer types (e.g., phased array and TOFD)
PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) guidelines for operators and personnel
Standards and Acceptance Criteria for UT
Overview of international standards: ASTM, ASME, ISO, and API for UT inspection
Acceptance criteria for different types of defects (e.g., crack size, porosity)
Documentation and reporting procedures for ultrasonic test results
Practical Demonstration and Hands-On Experience
Live demonstration of ultrasonic testing on sample materials (e.g., welds, pipes, and plates)
Hands-on experience for participants to conduct UT inspections using ultrasonic flaw detectors and transducers
Participants practice interpreting UT signals and identifying defects based on displayed waveforms
Reporting and Documentation in UT
Best practices for recording and documenting UT inspection results
Reporting formats for defect characterization, including location, size, and severity
Importance of traceability and proper documentation for compliance with industry standards
Show more
Course Details
This course provides an in-depth exploration of Ultrasonic Testing (UT), a versatile non-destructive testing (NDT) method that uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal defects and measure material properties. Combining theoretical knowledge with hands-on demonstrations, the course equips students with the skills needed to effectively perform and interpret UT inspections.

Show more
Course tags
Industry domains :
Aerospace , Automotive , HVACR
Engineering Disciplines :
FAQs on NDT (UT) Theory and Demonstration
Having specific question ? Ask now
mg
mani giri
13 days ago
Very useful for me I'm inthe welding inspection filed so very useful full notes and tips I get through this and learning also lot
Certificate of Mastery

Receive well recognised certificate that you can showcase on
Featured courses
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessmen...

How to prevent corrosion in the oil and ...

Application and use of "Green Hydrogen"

Career in EPC projects for Freshers

Career in EPC Cost Estimation

Learn MATLAB Programming

More Technical Courses From Chaitanya Purohit
Mastering Supply Chain Management: Optim...

Mastering Six Sigma: Driving Quality and...

Kaizen: The Art of Continuous Improvemen...

Welding Technology - Basics

Engineering Materials - Material Manufac...

Engineering Materials - Iron & Steel mak...

Engineering Materials - Material Classif...

Why NDT - Importance of Non Destructive ...

Similar Content Learn:
Introduction to Oil and Gas Well Logging...

Oil and Gas Well Completions

Lesson Learned

SWOT Analysis

Downhole Valves : Oil and Gas Well Compl...

Overview of Subsea Production Systems - ...

Introduction to Directional Drilling - O...

Similar Content Mentor:
All About Interviews

Presentation Skills _ Part 2

Similar Content Seminar:
7th International Oil & Gas Chemistry, C...

Similar Content Blogs:
Engineering Materials

The Importance of Steel in Construction

What is Piping Engineering?

Types of Piping Valves for Oil and Gas I...

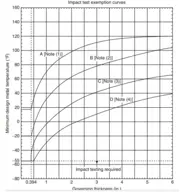
Technical Basis for Impact Test Exemptio...

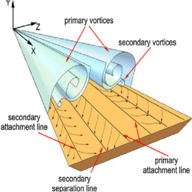
Aerodynamic physics of the Delta Wing

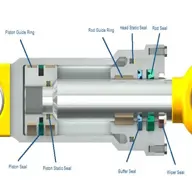
Seal of Hydraulic cylinder.

Similar Content Community:
Firefighting Design By Naga

Engineer's Corner

Cathodic protection

Corrosion

Cae engineers

Similar Profile:

Atul Kabre
Independent Consultant
BGS Group
The organiser of closed-d...

Anup Kumar Dey
Owner of https://whatispi...

Jyoti Swarup
--

Praveen Tiwari
--