Risk Based Inspection

Language
English
90 Views
Share
Coming in April, 2025
-
-
This course format is where trainer will explain you the subject via online live session. Date and time are not decided yet but it will be planned within next 2 weeks after you enroll & pay for this course. Get in touch with our team if any clarification is required.
₹ 499
online

₹ 499
Why do you enroll
Key topics covered
Course details
Course tags
Why do you enroll
Mastering Risk-Based Inspection can significantly enhance your career in industries like Oil and Gas, Chemical Processing, and Power Generation, leading to roles like Inspection Manager, Reliability Engineer, or Maintenance Manager, with median salaries ranging from $90,000 to over $160,000. By developing expertise in identifying and mitigating potential failures, you'll become a highly sought-after professional. This skillset enables you to optimize inspection schedules, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. As a certified expert in Risk-Based Inspection, you'll be highly valued for your ability to analyze risk, develop inspection strategies, and drive asset reliability. Your expertise will also enable you to take on leadership roles, develop and implement risk-based inspection programs, and drive business growth. By mastering Risk-Based Inspection, you'll unlock new career opportunities, build a strong professional reputation, and achieve long-term success.
Show more
Key topics covered
Introduction to Risk-Based Inspection (RBI)
Understanding the concept of RBI and its importance in asset management
The relationship between risk management and inspection planning
Key benefits of RBI: optimizing inspection resources, reducing downtime, and enhancing safety
Fundamentals of Risk Assessment
Introduction to risk assessment: identifying hazards, evaluating likelihood, and determining consequences
Quantifying risk: the concept of risk as the combination of probability and impact
Using risk matrices to assess and prioritize risks
RBI Methodology
The RBI process: asset identification, risk assessment, inspection planning, and decision-making
Key components of RBI: failure modes, consequence analysis, and probability of failure
The role of risk ranking in determining inspection frequency and scope
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Introduction to FMEA as a tool for identifying potential failure modes of assets
Analyzing the effects of different failures on asset performance and safety
How to use FMEA to prioritize inspection efforts and resources
Criticality and Consequence Analysis
Assessing the criticality of assets and their impact on operations, safety, and the environment
Understanding the consequence of failure (e.g., financial, environmental, operational)
How criticality analysis influences inspection schedules and maintenance priorities
Probability of Failure and Inspection Frequency
Techniques for estimating the probability of asset failure based on historical data, inspections, and operational conditions
Determining inspection frequency based on risk levels and asset condition
Balancing the risk of failure with the cost and frequency of inspections
Inspection Planning and Resource Allocation
Developing an inspection plan based on RBI results
Allocating resources effectively to high-risk areas
Optimizing inspection intervals and methodologies (e.g., non-destructive testing, visual inspection, corrosion monitoring)
Data Collection and Analysis for RBI
The role of data collection in risk-based inspection: asset history, condition monitoring, operational data
Analyzing data to identify trends and predict future asset behavior
Integrating data sources (inspection reports, sensor data, maintenance records) into the RBI process
Integrating RBI with Asset Integrity Management
How RBI fits into a broader asset integrity management (AIM) program
Ensuring alignment between RBI findings and maintenance, reliability, and safety strategies
The role of RBI in decision-making and continuous improvement
Regulatory Standards and Compliance in RBI
Understanding relevant RBI standards, codes, and regulations (e.g., API 580, ASME, ISO 55000)
Ensuring RBI processes comply with industry standards and regulatory requirements
Auditing and documentation requirements for RBI programs
Show more
Course Details
This course is designed to provide participants with a thorough understanding of Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) principles and methodologies. RBI is a strategic approach that prioritizes inspection resources and activities based on the risk associated with asset failure. Participants will learn how to implement RBI to optimize maintenance efforts, reduce downtime, and ensure the safety and reliability of assets.

Show more
Course tags
Industry domains :
Engineering Disciplines :
FAQs on Risk Based Inspection
Having specific question ? Ask now
mg
mani giri
2 months ago
Very useful for me I'm inthe welding inspection filed so very useful full notes and tips I get through this and learning also lot
Certificate of Mastery

Receive well recognised certificate that you can showcase on
Featured courses
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessmen...

How to prevent corrosion in the oil and ...

Application and use of "Green Hydrogen"

Career in EPC projects for Freshers

Career in EPC Cost Estimation

Learn MATLAB Programming

More Technical Courses From Chaitanya Purohit
Mastering Project Management: Delivering...

Mastering Supply Chain Management: Optim...

Mastering Six Sigma: Driving Quality and...

Kaizen: The Art of Continuous Improvemen...

Welding Technology - Basics

Engineering Materials - Material Manufac...

Engineering Materials - Iron & Steel mak...

Engineering Materials - Material Classif...

Similar Content Learn:
Basic of CMS IntelliCAD and GD&T

Fundamentals of Quality, QMS & ISO-9001

Buffer Tank - Basic, Concept, Design, Ca...

Business Excellence through Quality, QMS...

Similar Content Mentor:
All About Interviews

Presentation Skills _ Part 2

Similar Content Seminar:
The Petrochemical and Refining Congress:...
OIL & GAS AUTOMATION AND DIGITALISATION ...

7th International Oil & Gas Chemistry, C...

Similar Content Blogs:
Technical Basis for Impact Test Exemptio...

Aerodynamic physics of the Delta Wing

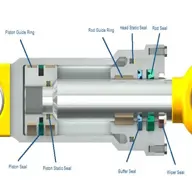
Seal of Hydraulic cylinder.

PRC Europe 2025: Italian Partners at the...
Similar Content Community:
Firefighting Design By Naga

Engineer's Corner

Cathodic protection

Corrosion

Cae engineers

Similar Profile:

Vijay Sachdev
Consultant - Project & Pr...

Debojyoti sen
MD & CEO, SAURYAJYOTI REN...

Sabari Kuppuraj
Engineer

Atul Kabre
Independent Consultant

Anup Kumar Dey
Owner of https://whatispi...

Jyoti Swarup
--

Praveen Tiwari
--

Please wait